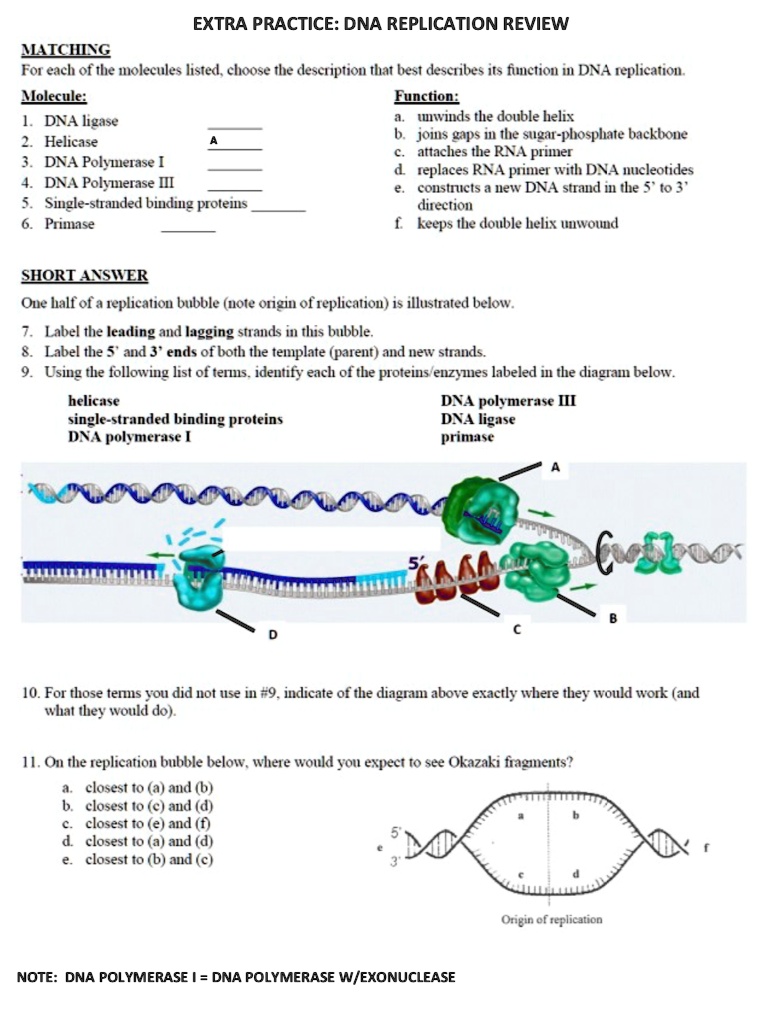
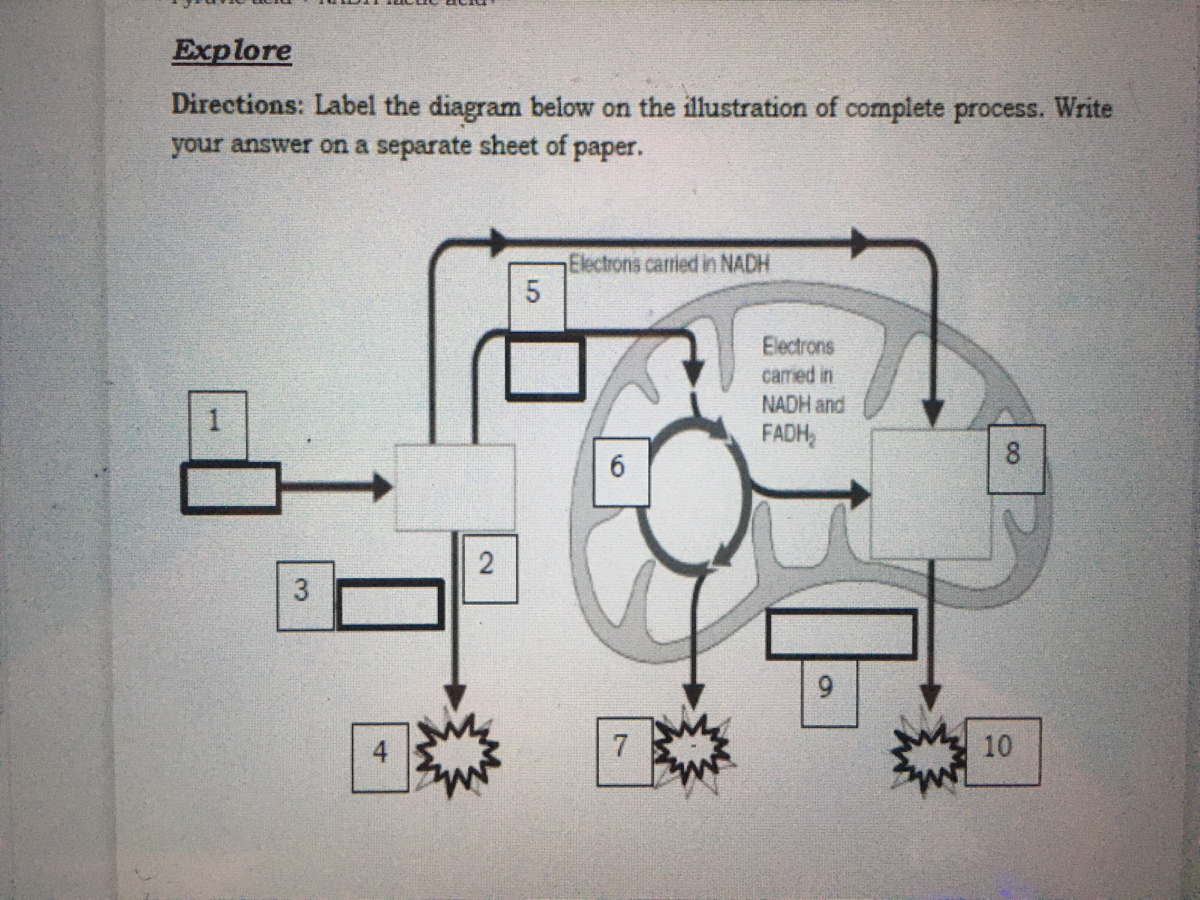
38 label each part of the atp molecule illustrated below
ATP-Student - ATP - ©HSPI - The POGIL Project Limited Use by Permission ... ATP atp (how do cells capture, release and store energy?) why? sporting goods store might accept bill for the purchase of bicycle, but the corner store will not ATP AND BIOLOGICAL ENERGY - Estrella Mountain Community College This covalent bond is known as a pyrophosphate bond. We can write the chemical reaction for the formation of ATP as: a) in chemicalese: ADP + Pi + energy ----> ATP. b) in English: Adenosine diphosphate + inorganic Phosphate + energy produces Adenosine Triphosphate. The chemical formula for the expenditure/release of ATP energy can be written as ...
Edexcel International GCSE (9-1) Biology Student Book by 17.12.2020 · 5 a Draw a diagram of a plant cell . Label all of the parts. Alongside each label write the function of that part. b Write down three differences between the cell you have drawn and a 'typical' animal cell. 6 Write a short description of the nature and function of enzymes. Include in your description: • a definition of an enzyme
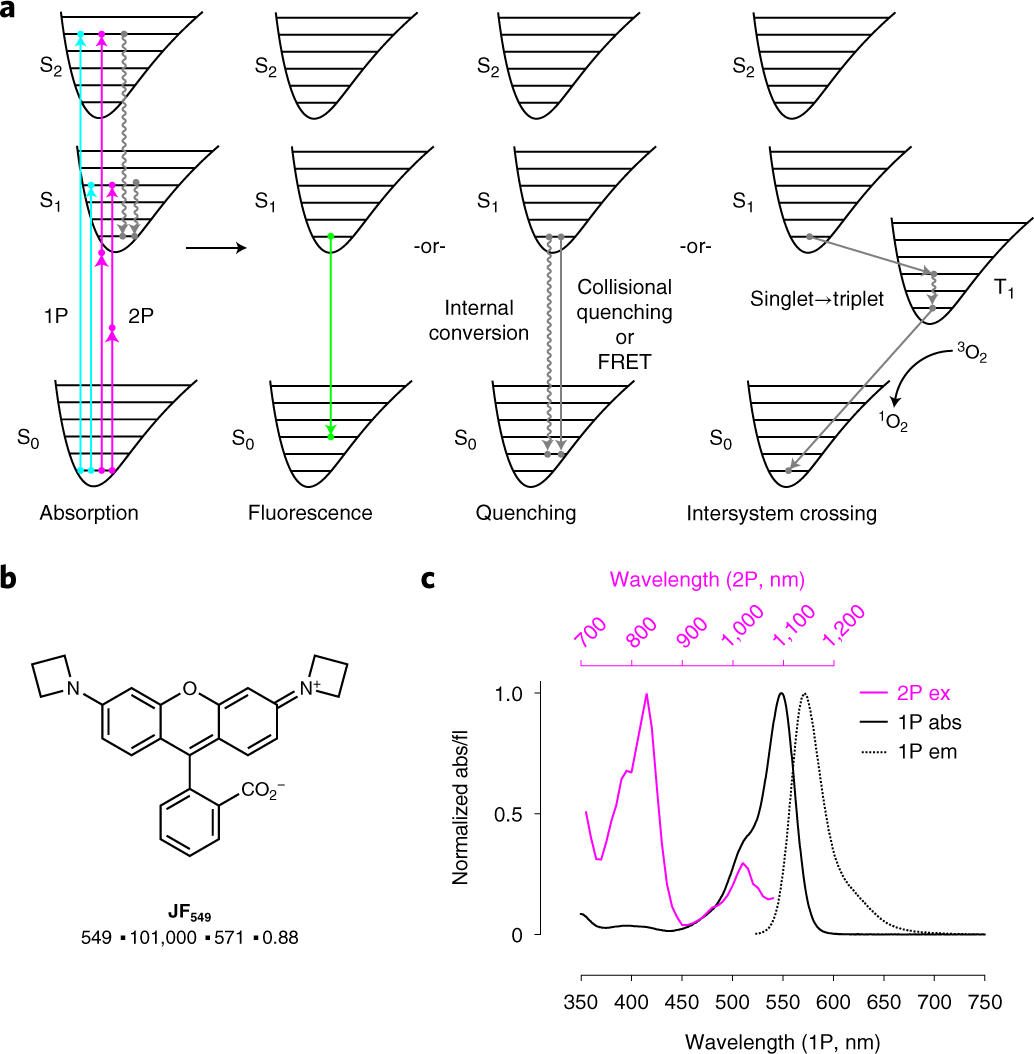
Label each part of the atp molecule illustrated below
Cambridge International AS and A Level Biology ... - Academia.edu BIO1: Maintaining a Balance 1. Most organisms are active in a limited temperature range IDENTIFY THE ROLE OF ENZYMES IN METABOLISM, DESCRIBE THEIR CHEMICAL COMPOSITION AND USE A SIMPLE MODEL TO DESCRIBE … Biochemistry PDF | PDF | Cell (Biology) | Biochemistry - Scribd The phosphate groups have a negative charge each at physiological pH, making RNA a charged molecule (polyanion). The bases may form hydrogen bonds between cytosine and guanine, between adenine and uracil and between guanine and uracil.[7] However, other interactions are possible, such as a group of adenine bases binding to each other in a bulge,[8] or the GNRA … Cellular Respiration Equation, Types, Stages, Products & Diagrams Cellular Respiration Equation: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + 38*ATP. 10. Cellular Respiration Equation: Every machine needs specific parts and fuel in order to function. Likewise, " biological machines " also require well engineered parts and good energy source in order to work. Perhaps the second most important molecule (DNA is the ...
Label each part of the atp molecule illustrated below. DOC Bio07_TR_U03_CH08.QXD - Pearson Education 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. 6. When a cell has energy available, how can it store small amounts of that energy? © Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. 63 Name Class Date 7. When is the energy stored in ATP released? 8. PDF Chapter 8 Photosynthesis, TE - Scarsdale Public Schools Chemical Energy and ATP(pages 202-203) 3. What is one of the principal chemical compounds that living things use to store energy? Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP 4. How is ATP different from ADP? ATP has three phosphate groups, while ADP has two phosphate groups. 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. Type Description Examples 2017-2018 - Science with Mrs. Floria - Google Below is the structural Formula for ATP (from Wikipedia). Notice the three phosphate molecules on the left. ... Be able to label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. 6. ... You must label the lungs, oral cavity, nasal cavity, larynx, trachea, bronchus, bronchioles, and diaphragm. (You may use the diagram below for help) X-ray crystallography - Wikipedia X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the …
Fatty acid - Wikipedia Fatty acids are classified in many ways: by length, by saturation vs unsaturation, by even vs odd carbon content, and by linear vs branched. Length of fatty acids. Short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) are fatty acids with aliphatic tails of five or fewer carbons (e.g. butyric acid).; Medium-chain fatty acids (MCFA) are fatty acids with aliphatic tails of 6 to 12 carbons, which can form medium … ATP BIS 2C.pdf - CONSERVATION OF ENERGY IN ATP By the end... - Course Hero ATP is a nucleotide composed of three general parts: a nitrogenous base, a sugar and three phosphate groups. a. Label the three parts of the nucleotide below. b. Draw an arrow to the two phosphoanhydride bonds in the ATP molecule. c. Write a balanced equation for the hydrolysis of one of the phosphoanhydride bonds in the ATP, indicate all ... PDF ATP - Loudoun County Public Schools ATP (How do cells capture, release and store energy?) Why? Model 1: The Structure of Adenosine Tri-Phosphate (ATP) 1. List the three parts of the ATP molecule and label each on the simplified molecule below. a. b. c. 2. Describe how you would be able to identify each part of the ATP molecule. Give yourself clues to identify each component. a. b. c. PDF Scarsdale Public Schools / Overview ATP has three Phosphate groups, while ADP has two phosphate groups. 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. Adenine Ribose 3 Phosphate groups p p 6. When a cell has energy available, how can it store small amounts of that energy? It can add a phosphate group to ADP molecules, producing ATP molecules. 7.
Molecular Biology, Robert Weaver, 5th Edition - Academia.edu Applications of recombinant DNA technology in gastrointestinal medicine and hepatology: Basic paradigms of molecular cell biology. Part C: Protein synthesis and post-translational processing in … Quantitative Chemical Proteomics Reveals New Potential Drug … 28.09.2011 · EGFR inhibition by the small molecule inhibitors lapatinib, gefitinib, and erlotinib as well as siRNA led to strong reduction of viability in high but not low expressing lines, confirming EGFR as a drug target in 10–20% of HNSCC cell lines. Similarly, high, but not low EPHA2-expressing cells showed strongly reduced viability concomitant with down-regulation of AKT … PDF haugfhs.weebly.com Chemical Energy and ATP (pages 202-203) 3. What is one of the principal chemical compounds that cells use to store energy? 4. How is ATP different from ADP? 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. P P p 6. When a cell has energy available, how can it store small amounts of that energy? A&p test 2 Flashcards | Quizlet -6CO2, 6H2O, 32 ATP -Pyruvic acid, lactic acid, 2 ATP -Pyruvic acid, 4 ATP -6CO2, 6H2O, 2 ATP 6CO2,6H20,32 ATP Exocrine glands can be further classified into------ glands, which are composed of a single epithelial cell, and----- glands, that are composed of many cells. unicellular, multicellular Extracellular matrix consist of lacunae and lamellae
Protein Digestion and Absorption – Nutrition: Science and … As illustrated in the image below, both mechanical and chemical digestion take place in the stomach. The stomach releases gastric juices containing hydrochloric acid and the enzyme, pepsin, which initiate the chemical digestion of protein. Muscular contractions, called peristalsis, also aid in digestion. The powerful stomach contractions churn the partially digested protein …
Solved Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule | Chegg.com Transcribed image text: Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule below. For Questions &-10, refer to the Visual Analogy comparing ATP to a charged battery. In the visual analogy, what chemical is represented by the low battery? What arc two ways in which the diagram shows an increase in energy? Describe the concepts shown in the diagram.
What are three parts of an ATP molecule? | Socratic Explanation: ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Also notable, ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. This molecule is composed of three parts: Adenine. Ribose. Three Phosphate Groups. Here is a picture:
PDF Chapter 8 Photosynthesis, SE - Loudoun County Public Schools Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. Type Description Examples Organisms that make their own food Organisms that obtain energy from the food they eat P P P 6. When a cell has energy available, how can it store small amounts of that energy? 7. When is the energy stored in ATP released? TYPES OF ORGANISMS © Pearson Education, Inc.
PDF TYPES OF ORGANISMS Type Description Examples - Mr. Adamosky's Biology Organisms that make their own food Organisms that obtain energy from the food they eat Chemical Energy and ATP (page 202) 3. What is one of the principal chemical compounds that cells use to store energy? 4. How is ATP different from ADP? 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. 6.
4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP Flashcards | Quizlet the type of molecule that is broken down which are carbohydrates,lipids, or proteins The breakdown of simple sugar glucose yields how many molecules of ATP? 36 What molecule is most commonly broken down to make ATP? carbohydrates How much energy does cabohydrates store? 4 calories per mg How much energy does lipids store? 9 calories per mg
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function This is a structural diagram of ATP. It is made up of the molecule adenosine (which itself is made up of adenine and a ribose sugar) and three phosphate groups. It is soluble in water and has a high energy content due to having two phosphoanhydride bonds connecting the three phosphate groups. Functions of ATP Energy Source
DOC 013368718X_CH08_115-128.indd - tesd.net of ATP are the key to its ability to store and supply energy. ATP releases energy when it breaks bonds between its phosphate groups. Most cells only store enough ATP for a few seconds of activity. Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule below. For Questions 8-10, refer to the Visual Analogy comparing ATP to a charged battery.
PDF Section 8-1 Energy and Life (pages 201-203) - Mystr Nakashima Organisms that make their own food Organisms that obtain energy from the food they eat P P P TYPES OF ORGANISMS Chemical Energy and ATP(page 202) 3. What is one of the principal chemical compounds that cells use to store energy? 4. How is ATP different from ADP? 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. 6.
atp molecule labeled - davincifireplace Label each part of the atp molecule illustrated below. In the yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe the FANCM-family DNA helicase FmI1 directs NCO recombination formation during meiosis. u Based on these helicase motifs, a number of helicase superfamilies have been distinguished. In: Spies, M.
SOLVED:VISUAL SKILLS This computer model shows the four parts of ATP ... VISUAL SKILLS This computer model shows the four parts of ATP synthase, each part consisting of a number of polypeptidelsubunits (the structure in gray is still an area of active research. Using Figure 9.14 as a guide, label the rotor, stator, internal rod, and catalytic knob of this molecular motor.
Cellular Respiration Diagram - Biology Wise The energy released is in the form of ATP molecules that are used to carry out various functions of the cell. The cellular respiration equation is as follows: C6H12O6 + O2 ――> H2O + CO2 + 36ATP. The following diagram of cellular respiration will give a better understanding of this process.
2-deoxyglucose transiently inhibits yeast AMPK signaling and … 11.08.2022 · Author summary In this article, we study the resistance to a drug named 2-deoxyglucose (2DG). 2DG is an efficient inhibitor of several metabolic pathways, particularly glycolysis which is of prime importance for tumor cell proliferation. Cancer cells but also cells from other organisms can develop various resistance strategies that only being unraveled. Here, …
PDF Section 8-1 Energy and Life - dps61.org 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. Type Description Examples Autotrophs Organisms that make their own food Plants Heterotrophs Organisms that obtain energy from Animals, mushrooms the food they eat Adenine Ribose 3 Phosphate groups P P P 6. When a cell has energy available, how can it store small amounts of that energy?
ATP POGIL.docx - ATP (How do cells capture, release, and store energy ... View ATP POGIL.docx from EXP 101 at C. Leon King High School. ATP (How do cells capture, release, and store energy?) Why? A sporting goods store might accept a $100 bill for the purchase of a
PDF Chapter 8 Photosynthesis Section 8-1 Energy and Life (pages 201-203) Organisms that make their own food Organisms that obtain energy from the food they eat P P P TYPES OF ORGANISMS Chemical Energy and ATP(page 202) 3. What is one of the principal chemical compounds that cells use to store energy? 4. How is ATP different from ADP? 5. Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. 6.
PDF Section 8-1 Energy and Life (pages 201-203) - Biology || Miss B Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. 6. When a cell has energy available, how can it store small amounts of that energy? ... Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about the light-dependent reactions. a. ... ATP synthase allows H+ to pass through the protein, causing the protein to rotate. As it rotates, it
PDF 4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP - Murrieta Valley Unified School District -up to 36 ATP from one glucose molecule adenosine triphosphate adenosine diphosphate tri=3 di=2 . 4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP • Fats store the most energy. -80 percent of the energy in your body -about 146 ATP from a triglyceride • Proteins are least likely to be broken down to make ATP.
Answered: Calculate the number of ATP for EACH… | bartleby Transcribed Image Text: Calculate the number of ATP for EACH and then circle the one that generates the most ATP 5 molecules of glucose in the presence of oxygen in an obligate aerobe A triglyceride with 3 52-Carbon chains A polypeptide with 5 amino acids 10 molecules of glucose in the absence of oxygen in an aerobe 10 molecules of glucose in an anaerobe
Kinds of Cell - Basic Unit Of Life - Google ATP is the vital energy molecule of all living systems which is absolutely necessary for key biochemical reactions within the cells. The actual synthesis of ATP from the coupling of ADP (adenosine diphosphate) with phosphate (PO 4) is very complicated and involves a mechanism calledchemiosmosis. The electron flow generates a higher ...
CH103 – Chapter 8: Homeostasis and Cellular Function – Chemistry 8.1 The Concept of Homeostasis. Homeostasis refers to the body’s ability to physiologically regulate its inner environment to ensure its stability in response to fluctuations in external or internal conditions.The liver, the pancreas, the kidneys, and the brain (hypothalamus, the autonomic nervous system and the endocrine system) help maintain homeostasis.
Cellular Respiration Equation, Types, Stages, Products & Diagrams Cellular Respiration Equation: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + 38*ATP. 10. Cellular Respiration Equation: Every machine needs specific parts and fuel in order to function. Likewise, " biological machines " also require well engineered parts and good energy source in order to work. Perhaps the second most important molecule (DNA is the ...
Biochemistry PDF | PDF | Cell (Biology) | Biochemistry - Scribd The phosphate groups have a negative charge each at physiological pH, making RNA a charged molecule (polyanion). The bases may form hydrogen bonds between cytosine and guanine, between adenine and uracil and between guanine and uracil.[7] However, other interactions are possible, such as a group of adenine bases binding to each other in a bulge,[8] or the GNRA …
Cambridge International AS and A Level Biology ... - Academia.edu BIO1: Maintaining a Balance 1. Most organisms are active in a limited temperature range IDENTIFY THE ROLE OF ENZYMES IN METABOLISM, DESCRIBE THEIR CHEMICAL COMPOSITION AND USE A SIMPLE MODEL TO DESCRIBE …
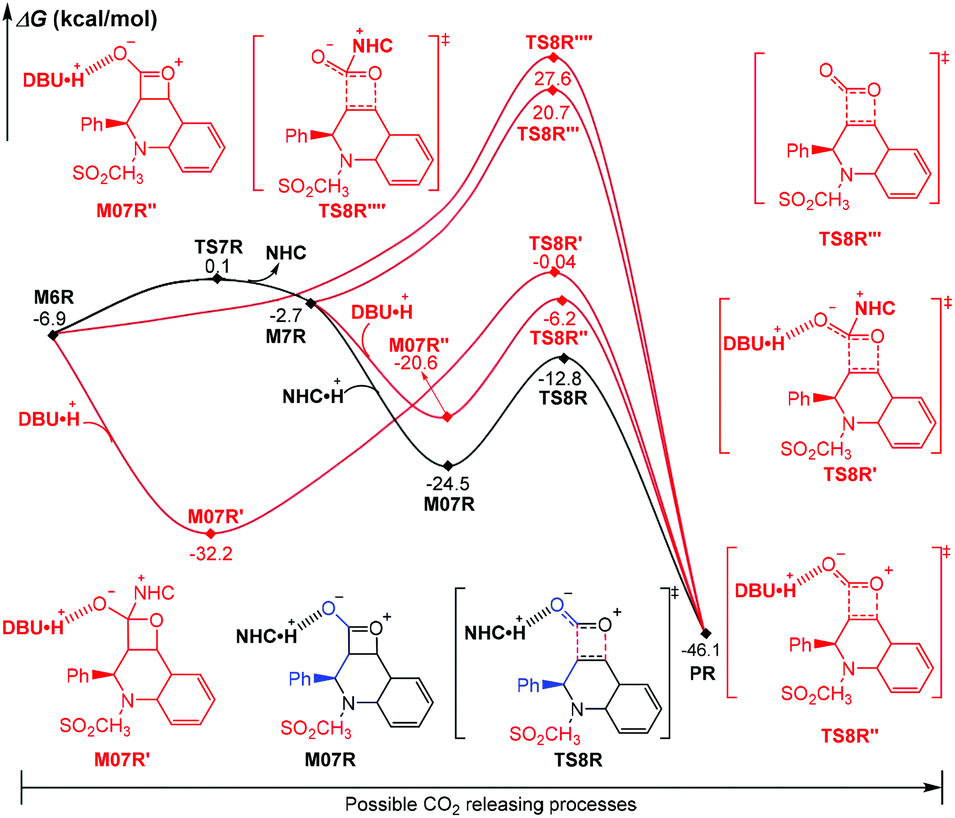





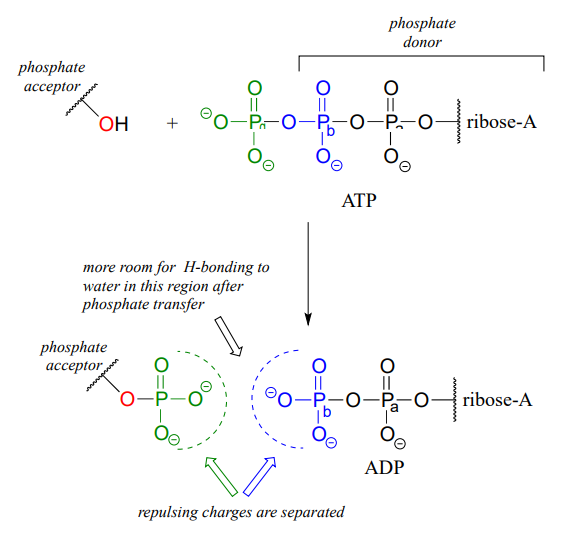


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-are-the-parts-of-nucleotide-606385-FINAL-5b76fa94c9e77c0025543061.png)















Post a Comment for "38 label each part of the atp molecule illustrated below"